National Interoperability Plan 101 | The Ultimate Guide
The long-awaited National Healthcare Interoperability Plan 2023-2028 aims to facilitate the safe and seamless sharing of consumer health information across Australia. It focuses on five priority areas, including identity, standards, information sharing, innovation and measuring benefits, with a total of 44 actions outlined. The Council for Connected Care has been created to oversee the plan's implementation and is responsible for monitoring and reporting on the progress of the actions. As a highly interoperable platform, Coviu summarises the key takeaways from this revolutionary step forward in digital healthcare.
An Australian History of Healthcare Interoperability
Throughout its history, Australia has made significant progress in healthcare interoperability, transitioning from paper-based records to digital systems and establishing national initiatives to promote secure data exchange and improve patient care. However, ongoing efforts and collaboration among stakeholders remain essential to address challenges and achieve the full potential of healthcare interoperability in the country. A timeline of how we have arrived at a National Healthcare Interoperability Plan can be seen below.
.png?width=1414&height=2000&name=Yellow%20Modern%20Project%20Timeline%20Document%20(A4).png)
The Purpose of the Legislation
The Interoperability Plan outlines a shared vision for long-term healthcare interoperability in Australia, addressing barriers and solutions between organisations. It recommends priority actions to increase interoperability, enhance workflows, accessibility and outcomes in healthcare, covering public, private and individual participants. The plan encompasses various care systems for physical, mental and social well-being, including healthcare, aged care, disability services and education. States and territories can adapt actions based on local needs and resources, with some initiatives being rolled out nationwide. Stakeholders from the health ecosystem will collaborate to ensure successful outcomes as actions are implemented over different timeframes.
The US 21st Century Cures Act served as a valuable reference for building the Australian National Healthcare Interoperability Plan. The Act, passed in 2016, is a significant piece of US legislation that mandates healthcare software vendors and providers to upgrade their technology to adopt common modern cloud-based healthcare data sharing standards. The Commonwealth government sees the potential benefits and impact of the American legislation and has aimed to replicate aspects of it in its own approach.
10 Principles of Interoperability
The National Healthcare Interoperability Plan outlines ten principles to expedite the transition toward a more interoperable national healthcare system. Embracing these principles and implementing digital health initiatives in line with them will advance the digital health maturity of the sector and pave the way for contemporary, innovative models of care. The 10 Principles driving the Plan state:
-
Health information is discoverable and accessible
-
Use of health information supports individual privacy, choice and safe access to information
-
National healthcare identifiers are used across the healthcare sector
-
National digital health standards and specifications are agreed and adopted
-
The value and quality of care is multiplied in a digitally connected health system
-
Measurement of digital health maturity informs interoperability system design
-
Core national healthcare digital infrastructure is used across the sector
-
Investment supports interoperability and an efficient health technology sector
-
Collaboration and stakeholder engagement underpins interoperability
-
High-quality data is critical for safe and meaningful interoperability
Key Focus Areas
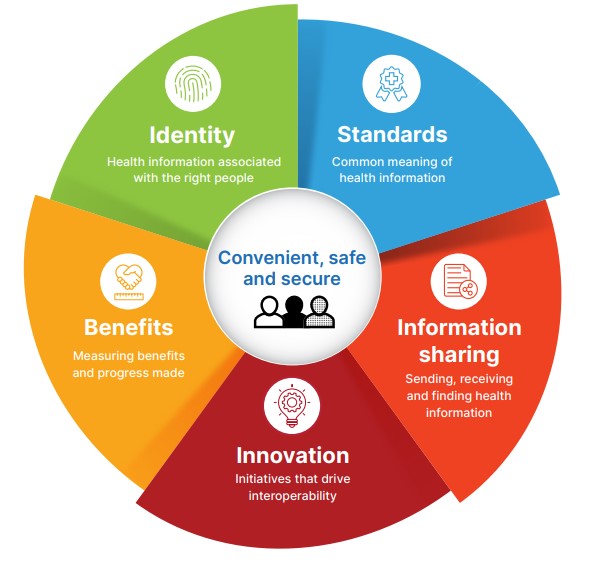
The National Healthcare Interoperability Plan is divided into five key focus areas to support the advancement of digital health interoperability in Australia. The focus areas correspond to a total of 44 actions designed to implement improved interoperability under each category. A description of each focus area can be found below.
Image: National Healthcare Interoperability Plan 2023-2028
-
Identity: Utilising the Healthcare Identifiers Service and the National Directory of Health Services (NHSD) to ensure accurate and unique identification of individuals, healthcare providers, and organisations during health information exchange.
-
Standards: Implementing effective leadership and sustainable governance for digital health standards, specifications and terminology. This aims to promote consistent and collaborative development, widespread adoption, and relevant conformity assessment schemes.
-
Information Sharing: Increasing the exchange of information between healthcare providers and individuals by ensuring information is easily discoverable, accessible and handled with consideration for safety, consent, privacy and data quality.
-
Innovation: Driving interoperability through future innovations, applying the interoperability principles to new digital health initiatives and functional enhancements.
-
Benefits: Measuring the digital health maturity of healthcare services to identify areas for investment that align with their strategic goals and the national digital health direction. Monitoring and evaluating the benefits of interoperability will inform progress and resource allocation.
Governance
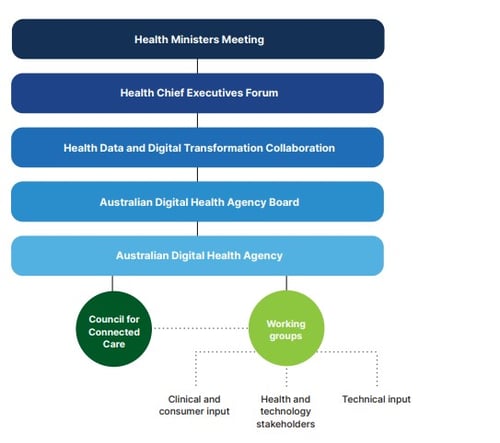
To administer and monitor the plan, a governance structure has been set up with clear lines of accountability. Ultimately the Australian Digital Health Agency and state/territory health departments are responsible for executing the Interoperability Plan under the Intergovernmental Agreement on National Digital Health. The Health Data and Digital Transformation Collaboration (HDDTC) will oversee implementation and report to the Health Chief Executives Forum. Annual progress reports will address emerging issues and potential changes to the plan's scope and timing. The Agency will establish a stakeholder advisory group for diverse input, and working groups may address specific issues.
Image: National Healthcare Interoperability Plan 2023-2028
Further, the Council for Connected Care, comprising of 27 leaders in Digital Health will play an important role in identifying and promoting ongoing opportunities in the industry for interoperability as they arise, as well as solutions to common challenges.
Current Challenges and Considerations
Achieving mature interoperability in Australia presents various barriers and challenges, such as limited use of national healthcare identifiers, difficulty in accessing comprehensive information about individuals, lack of trust in health information exchange security, unclear understanding of healthcare providers' obligations, commercial incentives favouring proprietary formats, insufficient policy drivers, legislative restrictions on healthcare identifiers, absence of a national governance system for standards, lack of agreed-upon information-sharing structures, cost challenges in upgrading legacy systems, and additional complexities in remote areas with limited digital connectivity.
The Plan recognises these challenges and attempts to address them through its comprehensive actions and focus areas.
A Step in The Right Direction
Coviu is enthusiastic about the launch of the National Healthcare Interoperability Plan. It believes that accurately identifying healthcare recipients and providers, standardising digital record-keeping, and enabling safe information sharing will lead to a more connected healthcare future. Coviu also emphasises the importance of empowering consumers to access their personal health information and control its access, which will further support the vision of a well-connected healthcare system.
Take your practice to the next level with Coviu
Find Out More About Coviu's Interoperability
Read more about Unlocking the Power of Interoperability with Coviu in our blog here.
Book a Demo
Why not get started with a free demo and let the team show you 1-1 how Coviu can work for you here.
Get Started with a Free Trial
To learn more about Coviu and how to implement telehealth into your practice start a free trial here.